





1 Motion (Uniform Motion And Non Uniform Motion, Acceleration and Velocity)
• A particle is a point-like object, has mass but infinitesimal size
• The object’s position is its location with respect to a chosen reference point, In the diagram, the road sign the reference point
• Motion occurs when an object changes its position. Both Distance and Time are important in describing motion.
• Sometimes you know motion has occurred even if you didn’t see it happen. (mail truck)
• Relative motion: when two objects are moving in a plane (either in same direction or opposite) each have relative motion with respect to second. e.g. a person sitting in a train and watching a tree, in this case tree is stable but is assumed to be moving but with respect to train.
Distance vs. Displacement
• Distance: How far an object has moved. It has only magnitude without direction. (total)
•Displacement: How far and in what direction an object has moved from its start position. i.e. the direct distance between two points. Speed
• Distance: How far an object has moved. It has only magnitude without direction. (total)
• Displacement: How far and in what direction an object has moved from its start position. i.e. the direct distance between two points.
Speed
![]()
• Speed = the distance an object travels in a given amount of time
• UI unit of speed is m/s
Types of Speed
• Constant speed: speed doesn’t change (set your car on cruise control)
• Changing speed: Riding a bike for 5 km. Take off and increase speed, slow down up hill, speed up down hill, stop for stop sign. The trip took you 15 min (.25 h)
![]()
• Instantaneous speed: speed at any given time.
Velocity
• Velocity: includes speed and DIRECTION
• Storm is moving at 20km/hr.
• Should you be seeking shelter?
• Suppose two trains are going with the same speed in opposite direction so they are having different velocities.
• Race car going around an oval track might have constant speed, but different velocities at each point.
Acceleration
• Any change in velocity over a period of time is called acceleration.
• The sign (+ or -) of indicates its direction. + sign shows the acceleration and – sign shows de-acceleration.
• Uniform (constant) acceleration equation
• a = v/t
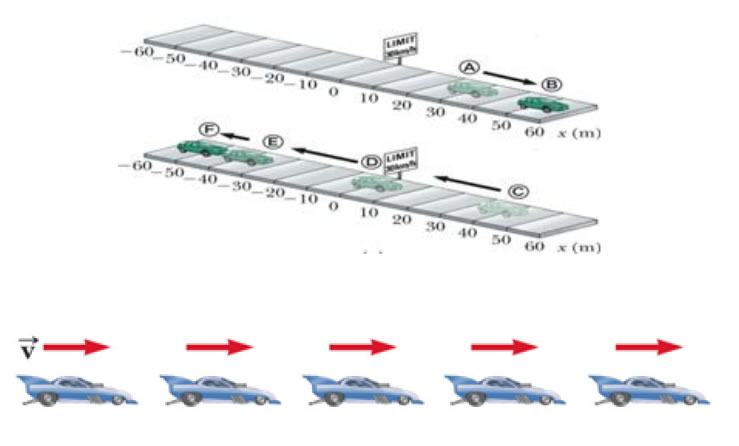
• Images of car are equally spaced.
• The car is moving with constant positive velocity (shown by red arrows maintaining the same size) .
• The acceleration equals to zero
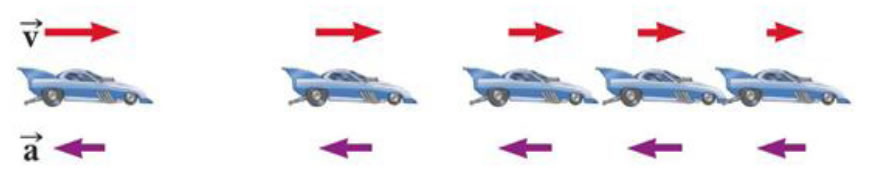
• Images of car become farther apart as time increase
• Velocity and acceleration are in the same direction
• Acceleration is uniform (Arrows below the car maintain the same length)
• Velocity is increasing (Arrows above the car are getting longer)
• This shows positive acceleration and positive velocity
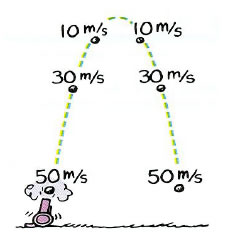
The instant speed at points of equal elevations is the same.
The velocities are different because they are in opposite
Free Fall & Air Resistance
 Galileo Galilei Italian physicist and astronomer Formulated laws of motion for objects in free fall
Galileo Galilei Italian physicist and astronomer Formulated laws of motion for objects in free fall
• A freely falling object is any object moving freely under the influence of gravity alone.
• It does not depend upon the initial motion of the object
• Dropped – released from rest
• Thrown downward
• Thrown upward
• The acceleration of an object in free fall is directed downward, regardless of the initial motion
• The magnitude of free fall acceleration (gravitational acceleration) is g = 9.80 m/s2
• g decreases with increasing altitude
• g varies with latitude, height and depth from earth surface.
• 9.80 m/s2 is the average at the Earth’s surface
• The italicized g will be used for the acceleration due to gravity
• Not to be confused with g for grams

• With negligible air resistance, falling objects can be considered freely falling.
objects of different shapes accelerate differently (stone vs feather)
• Speed both upward and downward
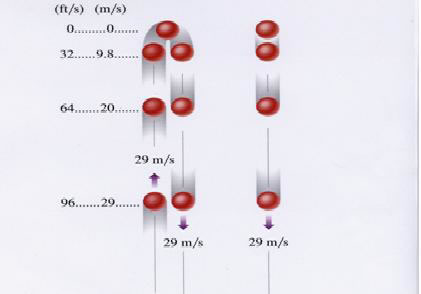
• The path is symmetrical.
• Acceleration is constant.
• The magnitude of the velocities is the same at equal heights.
• Images become closer together as time increases
• Acceleration and velocity are in opposite directions when ball goes upward.
• Acceleration is uniform (violet arrows maintain the same length)
• Velocity is decreasing in upward motion (red arrows are getting shorter)
• Positive velocity and negative acceleration
• Velocity becomes zero at maximum height.
• Time duration flight in going upward and coming back is always same.
Test Yourself :
1. What is SI Unit of displacement?
2. Name the quantity which represents rate of change of velocity.
3. A particle describes a semicircle of radius l 14m. What are its distance and displacement covered?
2 Graphical Representation Of Motion & Graphs (Refer to article 8.4 of NCERT text book.)
Test Yourself :
1. What does slope of Position – Time graph represent?
2. If velocity –time graph is parallel to time axis, what type of motion does it represent?
3 Equation of motion
(1) When object is moving in straight line-
• v = vo + at
• x = xo + vot + ½ at2
• v2 = vo2 + 2a(Δx)
• Average acceleration describes how fast the velocity is changing with respect to time.
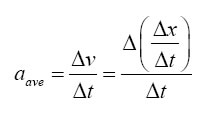
• where: aave = average acceleration
Δv = change in velocity
Δx = displacement
Δt = elapsed time
(2) when object is coming vertically downward-
•v = vo + gt
• h = vot + ½ gt2s
• v2 = vo2 + 2ah
(3) when object is coming vertically upward-
v = vo - gt
h = vot - ½ gt2
v2 = vo2 - 2gh
• The SI unit of velocity is the m/s.
Average accleration is + or – depending on direction.
• Instantaneous Acceleration
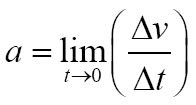
• Instantaneous acceleration is the limit of Δv/Δt as Δt approaches zero.
• Instantaneous acceleration is zero where slope is constant
• Instantaneous acceleration is positive where curve is concave up
• Instantaneous acceleration is negative where curve is concave down
Test Yourself :
1. Give the equation for uniform motion.
2. When a car stops after applying brakes, what is the final velocity?
4 Uniform Circular Motion
In this kind of motion the object moves on circle with fix speed but the direction is changed by the time so the velocity of the change so its called acceleration motion. This acceleration is called centrifugal acceleration. It is directed toward the centre.
Test Yourself:
1. What remains constant in uniform circular motion?
2. What changes continuously in uniform circular motion?
QUESTION BANK
One Mark questions
1. Can displacement be zero even when distance is not zero?
2. Can the distance travelled by an object be smaller than magnitude of its displacement?
3. A particle is moving with uniform velocity. What is its acceleration?
4. How can you get speed of an object from its distance – time graph?
5. How can you get distance of an object from its speed – time graph?
6. A brick & an elephant are in free fall. What is common in their motion?
7. When an object is thrown vertically upwards. What is its velocity at the highest point?
8. Can velocity & acceleration point in opposite directions?
9. Define acceleration.
10. What is non uniform motion?
Two Marks questions
1. Differentiate scalars & vectors?
2. What is retardation? How does it affect the speed?
3. Can speed of a body vary with its velocity constant? Explain.
4. Why is circular motion with constant speed called accelerated motion?
5. State the difference between distance & displacement.
6. What is the difference between speed & velocity?
7. What does a speedometer & odometer indicate?
Three Marks questions
1. If an object is thrown vertically upwards with speed 49 ms-1. How long does it take to complete upward journey? What maximum height does it achieve?
2. An object starting from rest covers 20 metres in first 2 seconds & 160 metres in next 4 seconds. What is its velocity after 7 seconds from the start?
Five Marks questions
1. Derive all the three equations of motion for uniform acceleration using graphical method.
2. A car a moving at rate of 72km/h and applies brakes which provide a retardation of 5ms-2.
(i) How much time does the car takes to stop.
(ii) How much distance does the car cover before coming to rest?
(iii) What would be the stopping distance needed if speed of the car is doubled?
.png)